Showing posts with label ubuntu 11.10. Show all posts
Showing posts with label ubuntu 11.10. Show all posts
Tuesday, 2 April 2013
Step By Step Turbo C++ IDE In Ubuntu 12.04
Well we are doing our labs based on the traditional Turbo C++ IDE and I decided to write this blog post with the information on how I installed it on my Ubuntu box.
First thing first, download Turbo C from internet. For your ease, I've uploaded it HERE.
We will have to install dosbox to run the windows dos mode applications so lets install it:
Once you install dosbox, unzip the content to somewhere in your $HOME directory. In my example, I unzipped the content of the Turbo C zip file into ~/Tools/TurboC3/. Now launch the dosbox by typing dosbox in the terminal. A dosbox emulation window will appear which will look like your old DOS system.
In the window, type the following (make sure you type appropriate path for your installation):
And, then follow the on-screen information. Refer to the screenshots below:
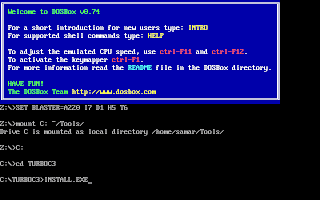
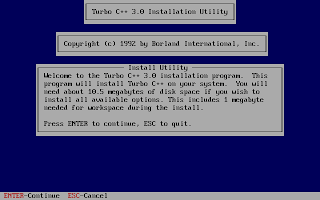
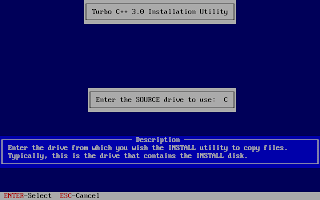
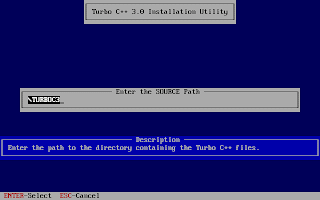
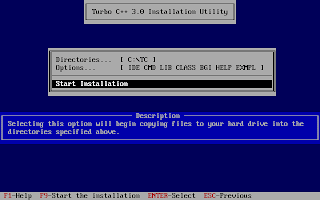
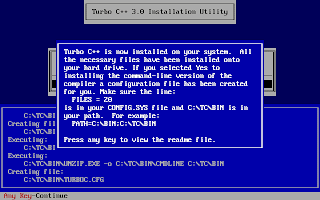
Once the installation finishes, you can then run the Turbo C by mounting the drive again and then navigation to C:\TC (cd C:\TC\BIN). If you need to use the Turbo C++ IDE frequently, my suggestion would be to add an autoexec entry in your dosbox configuration. The default configuration file resides in ~/.dosbox/dosbox-0.74.conf (My version of dosbox is 0.74 hence the file name, by default). Open up this file and in the section of [autoexec], add the lines below:
Adding this entry will run the above commands during the startup of dosbox thus giving you the Turbo C IDE interface directly on running dosbox.
I hope this helps :)
Read more...
First thing first, download Turbo C from internet. For your ease, I've uploaded it HERE.
We will have to install dosbox to run the windows dos mode applications so lets install it:
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ sudo apt-get install dosbox
Once you install dosbox, unzip the content to somewhere in your $HOME directory. In my example, I unzipped the content of the Turbo C zip file into ~/Tools/TurboC3/. Now launch the dosbox by typing dosbox in the terminal. A dosbox emulation window will appear which will look like your old DOS system.
In the window, type the following (make sure you type appropriate path for your installation):
mount C: ~/Tools/
C:
cd TurboC3
INSTALL.EXE
C:
cd TurboC3
INSTALL.EXE
And, then follow the on-screen information. Refer to the screenshots below:







Once the installation finishes, you can then run the Turbo C by mounting the drive again and then navigation to C:\TC (cd C:\TC\BIN). If you need to use the Turbo C++ IDE frequently, my suggestion would be to add an autoexec entry in your dosbox configuration. The default configuration file resides in ~/.dosbox/dosbox-0.74.conf (My version of dosbox is 0.74 hence the file name, by default). Open up this file and in the section of [autoexec], add the lines below:
[autoexec]
mount C: ~/Tools/
C:
cd TC\BIN
TC.EXE
mount C: ~/Tools/
C:
cd TC\BIN
TC.EXE
Adding this entry will run the above commands during the startup of dosbox thus giving you the Turbo C IDE interface directly on running dosbox.
I hope this helps :)
Read more...
Step By Step Turbo C++ IDE In Ubuntu 12.04
2013-04-02T21:40:00+05:45
Cool Samar
linux|linuxmint|tricks and tips|ubuntu 11.10|ubuntu 12.04|ubuntu 12.10|
Comments
Labels:
linux,
linuxmint,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu 11.10,
ubuntu 12.04,
ubuntu 12.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Tuesday, 29 January 2013
How To Check Which Groups You Belong To
In this post, you will get to know about a simple command that lets you know what groups the particular user belongs to. Users and groups are the one of the several concepts employed in the Linux systems for access control.
From the man page, the groups command does is:
Print group memberships for each USERNAME or, if no USERNAME is specified, for the current process (which may differ if the groups database has changed).
So if you are interested in finding what group a particular user is in, run the command as below. Replace samar with your USERNAME and you are good to go:
I hope this proves useful :)
Read more...
From the man page, the groups command does is:
Print group memberships for each USERNAME or, if no USERNAME is specified, for the current process (which may differ if the groups database has changed).
So if you are interested in finding what group a particular user is in, run the command as below. Replace samar with your USERNAME and you are good to go:
samar@Techgaun:~$ groups samar
samar : samar adm cdrom sudo vboxusers ....
samar : samar adm cdrom sudo vboxusers ....
I hope this proves useful :)
Read more...
How To Check Which Groups You Belong To
2013-01-29T18:55:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|linux|linuxmint|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
linux,
linuxmint,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Friday, 23 November 2012
Video Transcoding With HandBrake In Linux
HandBrake is a GPL-licensed, multiplatform, multithreaded video transcoder available for major platforms: linux, mac, and windows. HandBrake converts video from nearly any format to a handful of modern ones.
Handbrake can save output in two containers, MP4 and MKV and I've been using it as a MKV transcoder for a while and I'm quite satisfied with it. Even though the official wiki says its not a ripper, I can see it to be quite useful DVD ripper.
Handbrake is available in CLI (HandBrakeCLI) and GUI (ghb) mode. Hence this offers the flexibility to choose the appropriate version according to your linux personality. As of now, we can install HandBrake from PPA and the latest version is v. 0.9.8 released back in July this year.
HandBrake can be installed from PPA. Issue the following commands in your terminal
Or if you wish to install the GUI version, type:
I recommend using the CLI version since you can transcode/convert videos much more efficiently if you use the CLI version. But if you are not comfortable with the command line interfaces, the GUI version of HandBrake is also quite good.
Only problem I have felt is the naming convention of the commands for both the GUI and CLI versions of the tool. In order to run two versions of this tool, you need to type HandBrakeCLI for CLI version and ghb for the GUI version. The problem here is with the naming convention for the binaries. I mean, the names handbrake-cli and handbrake-gtk would be more straightforward than these badly chosen names. Otherwise, the tool does pretty good job of video conversion and can be good alternative if you are not comfortable with ffmpeg. Note that ffmpeg is also capable of video conversions of different formats and is a great tool. :)
Read more...
Handbrake can save output in two containers, MP4 and MKV and I've been using it as a MKV transcoder for a while and I'm quite satisfied with it. Even though the official wiki says its not a ripper, I can see it to be quite useful DVD ripper.
Handbrake is available in CLI (HandBrakeCLI) and GUI (ghb) mode. Hence this offers the flexibility to choose the appropriate version according to your linux personality. As of now, we can install HandBrake from PPA and the latest version is v. 0.9.8 released back in July this year.
HandBrake can be installed from PPA. Issue the following commands in your terminal
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:stebbins/handbrake-releases
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install handbrake-cli
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install handbrake-cli
Or if you wish to install the GUI version, type:
$ sudo apt-get install handbrake-gtk
I recommend using the CLI version since you can transcode/convert videos much more efficiently if you use the CLI version. But if you are not comfortable with the command line interfaces, the GUI version of HandBrake is also quite good.
Only problem I have felt is the naming convention of the commands for both the GUI and CLI versions of the tool. In order to run two versions of this tool, you need to type HandBrakeCLI for CLI version and ghb for the GUI version. The problem here is with the naming convention for the binaries. I mean, the names handbrake-cli and handbrake-gtk would be more straightforward than these badly chosen names. Otherwise, the tool does pretty good job of video conversion and can be good alternative if you are not comfortable with ffmpeg. Note that ffmpeg is also capable of video conversions of different formats and is a great tool. :)
Read more...
Video Transcoding With HandBrake In Linux
2012-11-23T22:43:00+05:45
Cool Samar
conversion tools|fedora|linux|linuxmint|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|ubuntu 12.04|ubuntu 12.10|video|
Comments
Labels:
conversion tools,
fedora,
linux,
linuxmint,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10,
ubuntu 12.04,
ubuntu 12.10,
video
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Saturday, 3 November 2012
Make Your Linux Read Papers For You
Fed up of reading text files and PDF papers? Is you eye power degrading day by day and can't hold even few minutes on screen? Don't worry, you can easily make your linux system speak and read all those papers for you.
There are several text to speech tools available for linux but in this post, I will be using festival, a Text-to-speech (TTS) tool written in C++. Also, Ubuntu and its derivation are most likely to include by default espeak, a multi-lingual software speech synthesizer.
For ubuntu and debian based system, type the following to install festival:
Moreover, you can also install a pidgin plugin that uses festival:
For now, you just need to install festival. Once you have installed festival, you can make it read text files for you. If you go through the online manual of festival, it says:
"Festival works in two fundamental modes, command mode and text-to-speech mode (tts-mode). In command mode, information (in files or through standard input) is treated as commands and is interpreted by a Scheme interpreter. In tts-mode, information (in files or through standard input) is treated as text to be rendered as speech. The default mode is command mode, though this may change in later versions."
To read a text file, you can use the command below:
The festival will start in text-to-speech (tts) mode and will read your text files for you. But now, we want to read PDF files and if you try to read PDF files directly (festival --tts paper.pdf), festival is most likely to speak the cryptic terms since it actually reads the content of PDF including its header (You know PDF is different than simple text file). So we will use a pdftotext command to convert our pdf file and then pipe the output to the festival so that festival reads the PDF files for us. You can use the syntax as below to read PDF files.
If you want to skip all those table of contents and prefaces or if you are in the middle of PDF, you can use the switches of pdftotext to change the starting and ending pages. For example, if I wish to read page 10 - 14 of a PDF, I would do:
Enjoy learning. I hope this post helps you ;)
Read more...
There are several text to speech tools available for linux but in this post, I will be using festival, a Text-to-speech (TTS) tool written in C++. Also, Ubuntu and its derivation are most likely to include by default espeak, a multi-lingual software speech synthesizer.
For ubuntu and debian based system, type the following to install festival:
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ sudo apt-get install festival
Moreover, you can also install a pidgin plugin that uses festival:
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ sudo apt-get install pidgin-festival
For now, you just need to install festival. Once you have installed festival, you can make it read text files for you. If you go through the online manual of festival, it says:
"Festival works in two fundamental modes, command mode and text-to-speech mode (tts-mode). In command mode, information (in files or through standard input) is treated as commands and is interpreted by a Scheme interpreter. In tts-mode, information (in files or through standard input) is treated as text to be rendered as speech. The default mode is command mode, though this may change in later versions."
To read a text file, you can use the command below:
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ festival --tts mypaper.txt
The festival will start in text-to-speech (tts) mode and will read your text files for you. But now, we want to read PDF files and if you try to read PDF files directly (festival --tts paper.pdf), festival is most likely to speak the cryptic terms since it actually reads the content of PDF including its header (You know PDF is different than simple text file). So we will use a pdftotext command to convert our pdf file and then pipe the output to the festival so that festival reads the PDF files for us. You can use the syntax as below to read PDF files.
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ pdftotext paper.pdf - | festival --tts
If you want to skip all those table of contents and prefaces or if you are in the middle of PDF, you can use the switches of pdftotext to change the starting and ending pages. For example, if I wish to read page 10 - 14 of a PDF, I would do:
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ pdftotext -f 10 -l 14 paper.pdf - | festival --tts
Enjoy learning. I hope this post helps you ;)
Read more...
Make Your Linux Read Papers For You
2012-11-03T11:05:00+05:45
Cool Samar
fedora|linux|linuxmint|text to speech|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|ubuntu 12.04|ubuntu 12.10|
Comments
Labels:
fedora,
linux,
linuxmint,
text to speech,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10,
ubuntu 12.04,
ubuntu 12.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Saturday, 27 October 2012
Linux Cat Command Examples
The cat command displays the content of file on the standard output. If multiple files are specified, the contents of all files will be concatenated and then displayed on the standard output. Likewise, if no file is specified, it will assume standard input (keyboard input) as the input to the command. The Ctrl + d is the shortcut used to save the contents in the appropriate output placeholder specified and exit the cat command.
Print content of file in standard output
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat workers.txt List of workers, designations & salary (in K): Kshitiz Director 30 Bikky Manager 20 Abhis Sweeper 10 Rajesh Guard 12
Print line numbers
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat -n workers.txt
1 List of workers, designations & salary (in K):
2 Kshitiz Director 30
3 Bikky Manager 20
4
5
6 Abhis Sweeper 10
7 Rajesh Guard 12
Print line numbers for non-empty lines only
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat -b workers.txt
1 List of workers, designations & salary (in K):
2 Kshitiz Director 30
3 Bikky Manager 20
4 Abhis Sweeper 10
5 Rajesh Guard 12
Create a new file
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat > newfile.txt We can create text files using cat command once u finish writing, press ctrl+d to save file ^d
Display content of multiple files
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat workers.txt newfile.txt List of workers, designations & salary (in K): Kshitiz Director 30 Bikky Manager 20 Abhis Sweeper 10 Rajesh Guard 12 We can create text files using cat command once u finish writing, press ctrl+d to save file
Combine multiple files to new file
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat workers.txt newfile.txt > concat.txt samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat concat.txt List of workers, designations & salary (in K): Kshitiz Director 30 Bikky Manager 20 Abhis Sweeper 10 Rajesh Guard 12 We can create text files using cat command once u finish writing, press ctrl+d to save file
Append data to existing file
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat >> newfile.txt New line added ^d samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat newfile.txt We can create text files using cat command once u finish writing, press ctrl+d to save file New line added
Alternatively, you can use the syntax below if you wish to create new file combining the content of already existing file and standard input.
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat newfile.txt - > myfile thanks for everything ^d samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat myfile We can create text files using cat command once u finish writing, press ctrl+d to save file New line added thanks for everything
Another possibility is to combine two text files with data from standard input (keyboard) in-between the contents of these two text files.
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat workers.txt - newfile.txt > myfile ---------------------------------- ^d samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat myfile List of workers, designations & salary (in K): Kshitiz Director 30 Bikky Manager 20 Abhis Sweeper 10 Rajesh Guard 12 ---------------------------------- We can create text files using cat command once u finish writing, press ctrl+d to save file New line added
Display $ sign at the end of each line
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat -E workers.txt List of workers, designations & salary (in K):$ Kshitiz Director 30$ Bikky Manager 20$ $ $ Abhis Sweeper 10$ Rajesh Guard 12$
Display ^I sign instead of TABs
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat -T workers.txt List of workers, designations & salary (in K): Kshitiz^IDirector^I30 Bikky^IManager^I^I20 Abhis^ISweeper^I^I10 Rajesh^IGuard^I^I12
Display files with non-printing characters
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat -v /bin/nc
In the example above, the non-printing characters are replaced with ^ and M- notation except for line breaks and TABs. This can be used to display the contents of binary files which would otherwise have shown gibberish text all over the console.
Show contents with tabs, line breaks and non-printing characters
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat -A /bin/nc
The tab will be substituted by ^I, line breaks with $ and non-printing characters with ^ and M- notation. Actually, the -A switch is equivalent to -vET switch.
Supress/squeeze repeated empty lines
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat -s workers.txt List of workers, designations & salary (in K): Kshitiz Director 30 Bikky Manager 20 Abhis Sweeper 10 Rajesh Guard 12
Using -s switch, we can squeeze repeatedly occurring blank lines and replace all the adjacent empty lines with a single empty line in the output. This might be useful to reformat a file with several empty lines in-between (eg. cat -s workers.txt > formatted_workers.txt).
Display last line first
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ tac workers.txt Rajesh Guard 12 Abhis Sweeper 10 Bikky Manager 20 Kshitiz Director 30 List of workers, designations & salary (in K):
It is the tac, not the cat that is doing the magic but just thought that this is the right place to make a note about this little known command.
Edit: Added here-doc examples. Thanks rho dai for pointing me this.
Parameter substitution using here-document strings
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat > test << TEST samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ I am $USER. My home is $HOME samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ I came here from $OLDPWD samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ TEST samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat test I am samar. My home is /home/samar I came here from /home/samar/Downloads
Command expansion example
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat > test << TEST samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ $(ls /) samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ TEST samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat test bin boot cdrom dev etc home initrd.img initrd.img.old lib lost+found media mnt opt proc root run sbin selinux srv sys tmp usr var vmlinuz vmlinuz.old
Parameter substitution turned off
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat > test << 'TEST' samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ I am $USER. My home is $HOME samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ I came here from $OLDPWD samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ TEST samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat test I am $USER. My home is $HOME I came here from $OLDPWD
Note the difference between the last example and previous two examples. Enclosing the limit string TEST with quotes prevents the substitutions and expansions.
I hope these examples are useful. :)
Read more...
Linux Cat Command Examples
2012-10-27T14:17:00+05:45
Cool Samar
bash|command line|fedora|linux|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|ubuntu 12.04|ubuntu 12.10|unix|
Comments
Labels:
bash,
command line,
fedora,
linux,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10,
ubuntu 12.04,
ubuntu 12.10,
unix
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Monday, 22 October 2012
Ubuntu Tweak Development Will Continue
Three days ago, Ubuntu Tweak developer Tualatrix had posted a blog post mentioning that the Ubuntu Tweak will no longer be developed but he has now changed his mind and has decided to continue the development because of support he received.
The developer writes
You made me know that Ubuntu Tweak is still valuable, and as the first software project I made 5 years ago, it is just like my baby, I don’t really want to give up the development.
and thanks all the good people who left the message for him and forked the app in github.
The blog post also mentions
Back to 5 years ago, I developed it just because of my practice on Linux programming, I felt freedom when I make things on Linux (Although I didn’t have developing experience on Windows and Mac then). But now I don’t feel any freedom about developing this software any more. The initial motivation is changed, and I’m still looking for new motivation.
Overall, he is not too satisfied with his current overload for working on this personal project while still managing time for his job and personal life.
Anyway, Ubuntu Tweak 0.8.1 is out and you can download from PPA.
PPA DEB link
Release Notes
Read more...
The developer writes
You made me know that Ubuntu Tweak is still valuable, and as the first software project I made 5 years ago, it is just like my baby, I don’t really want to give up the development.
and thanks all the good people who left the message for him and forked the app in github.
The blog post also mentions
Back to 5 years ago, I developed it just because of my practice on Linux programming, I felt freedom when I make things on Linux (Although I didn’t have developing experience on Windows and Mac then). But now I don’t feel any freedom about developing this software any more. The initial motivation is changed, and I’m still looking for new motivation.
Overall, he is not too satisfied with his current overload for working on this personal project while still managing time for his job and personal life.
Anyway, Ubuntu Tweak 0.8.1 is out and you can download from PPA.
PPA DEB link
Release Notes
Read more...
Ubuntu Tweak Development Will Continue
2012-10-22T16:52:00+05:45
Cool Samar
news|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|ubuntu 12.04|ubuntu 12.10|ubuntu tweak|
Comments
Labels:
news,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10,
ubuntu 12.04,
ubuntu 12.10,
ubuntu tweak
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Saturday, 13 October 2012
Empty Trash From Command Line In Ubuntu
CLI is such a sexy piece so why bother using GUI, even for cleaning up your trash. In this post, you will see how you can empty trash in Ubuntu from command line.
The trash you see in GUI is nothing but just the view for the files deleted by users which are temporarily moved to the special location of user's home directory. For any user, the trash location is ~/.local/share/Trash/. That is, whatever a user deletes gets saved in this location.
I hope this becomes useful :)
Read more...
The trash you see in GUI is nothing but just the view for the files deleted by users which are temporarily moved to the special location of user's home directory. For any user, the trash location is ~/.local/share/Trash/. That is, whatever a user deletes gets saved in this location.
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ rm -rf ~/.local/share/Trash/
I hope this becomes useful :)
Read more...
Empty Trash From Command Line In Ubuntu
2012-10-13T16:11:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|ubuntu 12.04|ubuntu 12.10|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10,
ubuntu 12.04,
ubuntu 12.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Enable Fingerprint Authentication In Ubuntu
So you got fingerprint reader in your device but have not been able to use it under ubuntu? Follow this How To to enable fingerprint authentication in ubuntu using the Fingerprint GUI from fingerprints reader integration team.
First make sure your fingerprint hardware is supported. You can check for the vendor and device ID by entering the following command:
This link provides the list of the supported fingerprint readers.
Installation is easy. Fire up the terminal and enter the following commands:
You will have to restart the system or log out the session and login back to use and configure the fingerprint GUI.
Press Alt + F2 and type fingerprint-gui. From this GUI, you can configure and enroll your fingerprints.
Read more...
First make sure your fingerprint hardware is supported. You can check for the vendor and device ID by entering the following command:
samar@TG:~$ lsusb | grep -i finger | awk -F " " '{print $6}'
138a:0005
138a:0005
Installation is easy. Fire up the terminal and enter the following commands:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:fingerprint/fingerprint-gui
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install libbsapi policykit-1-fingerprint-gui fingerprint-gui
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install libbsapi policykit-1-fingerprint-gui fingerprint-gui
You will have to restart the system or log out the session and login back to use and configure the fingerprint GUI.
Press Alt + F2 and type fingerprint-gui. From this GUI, you can configure and enroll your fingerprints.
Read more...
Enable Fingerprint Authentication In Ubuntu
2012-10-13T10:11:00+05:45
Cool Samar
fingerprint|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|ubuntu 12.10|
Comments
Labels:
fingerprint,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10,
ubuntu 12.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Monday, 3 September 2012
Preventing Accidental Overwriting Of Files In Bash Shell
How many times has this happened to you? It used to happen once in a while with me. A Linux user learns to use the redirection operators such as '>' and '>>' but accidental overwriting starts to become common in commands you use and shell scripts you write.
The accidental overwriting of files that happens unintentionally is known as clobbering and it commonly happens while using the '>' redirection operator.
In the above example, the mycmd clobbers any existing data in the myfile file if that file exists already. Worse things may happen sometime. Imagine accidentally typing
instead of possibly using other redirection operators (like >> or <). Thankfully, you could recover /etc/passwd from either /etc/passwd- or /var/backups/passwd.bak if you hadn't rm'd these files.
To prevent such accidental overwriting, we can set the noclobber environment variable. Below is a session of enabling this variable:
As seen above, you have to turn on the noclobber variable using the set -o noclobber command in your shell. However, you might want to intentionally overwrite contents of certain files even when the noclobber is turned on.
Notice the >| in place of your normal > redirection operator. Using this operator, you can however overwrite the existing files even if the noclobber is turned on.
If you want to turn off the noclobber variable, type the following:
You can also permanently turn on the noclobber by the following command:
Moreover, such accidental overwriting can be prevented by enabling the interactive mode which is available in most of the linux commands. For example, you can write the alias for many commands that are likely to cause accidental overwriting. See some examples of aliases below:
You could even keep these aliases in your ~/.bashrc file permanently. Enabling such interactive modes by default in the commands that are more likely to cause accidental overwriting can prevent clobbering in many cases.
I hope this proves useful to you :)
Read more...
The accidental overwriting of files that happens unintentionally is known as clobbering and it commonly happens while using the '>' redirection operator.
samar@Techgaun:~$ mycmd > myfile
In the above example, the mycmd clobbers any existing data in the myfile file if that file exists already. Worse things may happen sometime. Imagine accidentally typing
samar@Techgaun:~$ mycmd > /etc/passwd
instead of possibly using other redirection operators (like >> or <). Thankfully, you could recover /etc/passwd from either /etc/passwd- or /var/backups/passwd.bak if you hadn't rm'd these files.
To prevent such accidental overwriting, we can set the noclobber environment variable. Below is a session of enabling this variable:
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ echo "www.techgaun.com" > myfile
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ echo "Overwriting techgaun.com" > myfile
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ set -o noclobber
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ echo "Retrying to overwrite" > myfile
-bash: myfile: cannot overwrite existing file
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ echo "Overwriting techgaun.com" > myfile
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ set -o noclobber
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ echo "Retrying to overwrite" > myfile
-bash: myfile: cannot overwrite existing file
As seen above, you have to turn on the noclobber variable using the set -o noclobber command in your shell. However, you might want to intentionally overwrite contents of certain files even when the noclobber is turned on.
samar@Techgaun:~$ mycmd >| myfile
Notice the >| in place of your normal > redirection operator. Using this operator, you can however overwrite the existing files even if the noclobber is turned on.
If you want to turn off the noclobber variable, type the following:
samar@Techgaun:~$ set +o noclobber
You can also permanently turn on the noclobber by the following command:
samar@Techgaun:~$ echo "set -o noclobber" >> ~/.bashrc
Moreover, such accidental overwriting can be prevented by enabling the interactive mode which is available in most of the linux commands. For example, you can write the alias for many commands that are likely to cause accidental overwriting. See some examples of aliases below:
samar@Techgaun:~$ alias rm=rm -i
samar@Techgaun:~$ alias mv=mv -i
samar@Techgaun:~$ alias mv=mv -i
You could even keep these aliases in your ~/.bashrc file permanently. Enabling such interactive modes by default in the commands that are more likely to cause accidental overwriting can prevent clobbering in many cases.
I hope this proves useful to you :)
Read more...
Preventing Accidental Overwriting Of Files In Bash Shell
2012-09-03T22:56:00+05:45
Cool Samar
bash|command line|fedora|filesystem|linux|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
bash,
command line,
fedora,
filesystem,
linux,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Monday, 27 August 2012
Install XAMPP 1.8 From PPA In Ubuntu
Since apache friends has released the v. 1.8 of XAMPP for linux and windows, its important you guys upgrade your XAMPP. In this post, you will find the instructions to install XAMPP 1.8 from PPA.
The most important updates of v. 1.8.0 of XAMPP are: Apache 2.4.2, MySQL 5.5.25a, PHP 5.4.4, and phpMyAdmin 3.5.1. Since the software components are updated, I strongly recommend to upgrade your XAMPP.
All you have to do is follow the following steps in order:
Alternatively, you can download the tar file for XAMPP from Apache Friends and follow their instructions to install XAMPP 1.8.0. In case you're looking for upgrading your previous XAMPP installation, be sure to follow this How To.
I hope this helps :)
Read more...
The most important updates of v. 1.8.0 of XAMPP are: Apache 2.4.2, MySQL 5.5.25a, PHP 5.4.4, and phpMyAdmin 3.5.1. Since the software components are updated, I strongly recommend to upgrade your XAMPP.
All you have to do is follow the following steps in order:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:upubuntu-com/xampp
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install xampp
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install xampp
Alternatively, you can download the tar file for XAMPP from Apache Friends and follow their instructions to install XAMPP 1.8.0. In case you're looking for upgrading your previous XAMPP installation, be sure to follow this How To.
I hope this helps :)
Read more...
Install XAMPP 1.8 From PPA In Ubuntu
2012-08-27T22:56:00+05:45
Cool Samar
apache|linux|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|xampp|
Comments
Labels:
apache,
linux,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10,
xampp
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
How To Manually Install Flash Player 11 In Linux
This post will provide a step by step instructions for installing flash player 11 plugin in ubuntu 11.04 and other different versions and distros. This will be helpful for everybody who are having trouble with the software center like I had.
Make sure no firefox process is running and then fire up the terminal and type the following commands in order:
Once you have finished copying the shared object and other necessary files in their respective target directories, you can open the firefox and you're good to go. :)
Read more...
Make sure no firefox process is running and then fire up the terminal and type the following commands in order:
mkdir -p ~/flash && cd ~/flash
wget http://archive.canonical.com/pool/partner/a/adobe-flashplugin/adobe-flashplugin_11.2.202.238.orig.tar.gz
tar -zxvf adobe-flashplugin_11.2.202.238.orig.tar.gz
sudo cp -r libflashplayer.so /usr/lib/firefox/plugins
sudo cp -r usr/* /usr
wget http://archive.canonical.com/pool/partner/a/adobe-flashplugin/adobe-flashplugin_11.2.202.238.orig.tar.gz
tar -zxvf adobe-flashplugin_11.2.202.238.orig.tar.gz
sudo cp -r libflashplayer.so /usr/lib/firefox/plugins
sudo cp -r usr/* /usr
Once you have finished copying the shared object and other necessary files in their respective target directories, you can open the firefox and you're good to go. :)
Read more...
How To Manually Install Flash Player 11 In Linux
2012-08-27T22:22:00+05:45
Cool Samar
fedora|internet|linux|mozilla firefox|plugin|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|web|
Comments
Labels:
fedora,
internet,
linux,
mozilla firefox,
plugin,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10,
web
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Monday, 13 August 2012
Screen Recording Software Solutions For Linux
Windows users have several options to choose from when it comes to the desktop recording (and only paid ones are good generally) but Linux users have fewer options but robust, simple, and best of all, free and open source desktop screen recording tools that we can trust on.
Below are some of the screen recording tools you might want to try:
recordMyDesktop is a desktop session recorder for GNU/Linux written in C. recordMyDesktop itself is a command-line tool and few GUI frontends are also available for this tool. There are two frontends, written in python with pyGtk (gtk-recordMyDesktop) and pyQt4 (qt-recordMyDesktop). recordMyDesktop offers also the ability to record audio through ALSA, OSS or the JACK audio server. Also, recordMyDesktop produces files using only open formats. These are theora for video and vorbis for audio, using the ogg container.
Installation under debian and ubuntu:
XVidCap is a small tool to capture things going on on an X-Windows display to either individual frames or an MPEG video. It enables you to capture videos off your X-Window desktop for illustration or documentation purposes.It is intended to be a standards-based alternative to tools like Lotus ScreenCam.
Istanbul is a desktop session recorder for the Free Desktop. It records your session into an Ogg Theora video file. To start the recording, you click on its icon in the notification area. To stop you click its icon again. It works on GNOME, KDE, XFCE and others. It was named so as a tribute to Liverpool's 5th European Cup triumph in Istanbul on May 25th 2005.
Vnc2flv is a cross-platform screen recording tool for UNIX, Windows or Mac. It captures a VNC desktop session (either your own screen or a remote computer) and saves as a Flash Video (FLV) file.
Wink is a Tutorial and Presentation creation software, primarily aimed at creating tutorials on how to use software (like a tutor for MS-Word/Excel etc). Using Wink you can capture screenshots, add explanations boxes, buttons, titles etc and generate a highly effective tutorial for your users. It requires GTK 2.4 or higher and unfortunately is just a freeware(could not find any source code for it).
Screenkast is a screen capturing program that records your screen-activities, supports commentboxes and exports to all video formats.
If you got any more suggestions, please drop the comment. :)
Read more...
Below are some of the screen recording tools you might want to try:
recordMyDesktop
recordMyDesktop is a desktop session recorder for GNU/Linux written in C. recordMyDesktop itself is a command-line tool and few GUI frontends are also available for this tool. There are two frontends, written in python with pyGtk (gtk-recordMyDesktop) and pyQt4 (qt-recordMyDesktop). recordMyDesktop offers also the ability to record audio through ALSA, OSS or the JACK audio server. Also, recordMyDesktop produces files using only open formats. These are theora for video and vorbis for audio, using the ogg container.
Installation under debian and ubuntu:
sudo apt-get install gtk-recordmydesktop
XVidCap
XVidCap is a small tool to capture things going on on an X-Windows display to either individual frames or an MPEG video. It enables you to capture videos off your X-Window desktop for illustration or documentation purposes.It is intended to be a standards-based alternative to tools like Lotus ScreenCam.
sudo apt-get install xvidcap
Istanbul
Istanbul is a desktop session recorder for the Free Desktop. It records your session into an Ogg Theora video file. To start the recording, you click on its icon in the notification area. To stop you click its icon again. It works on GNOME, KDE, XFCE and others. It was named so as a tribute to Liverpool's 5th European Cup triumph in Istanbul on May 25th 2005.
sudo apt-get install istanbul
Vnc2Flv
Vnc2flv is a cross-platform screen recording tool for UNIX, Windows or Mac. It captures a VNC desktop session (either your own screen or a remote computer) and saves as a Flash Video (FLV) file.
Wink
Wink is a Tutorial and Presentation creation software, primarily aimed at creating tutorials on how to use software (like a tutor for MS-Word/Excel etc). Using Wink you can capture screenshots, add explanations boxes, buttons, titles etc and generate a highly effective tutorial for your users. It requires GTK 2.4 or higher and unfortunately is just a freeware(could not find any source code for it).
Screenkast
Screenkast is a screen capturing program that records your screen-activities, supports commentboxes and exports to all video formats.
If you got any more suggestions, please drop the comment. :)
Read more...
Screen Recording Software Solutions For Linux
2012-08-13T17:21:00+05:45
Cool Samar
fedora|linux|software|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|video|
Comments
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Wednesday, 18 July 2012
Why Alias Command With Itself
Aliasing the command to itself to suppress the original functionality of the command and provide it new added sets of functionality can come quite handy for linux users and administrators.
If you have been using linux shell for a while, I'm pretty sure you are now familiar with the `ls` command, if not I think you have just learnt to use man pages. Probably you've been using `ls -l` command to list files with the files size as well. Too bad, you won't just be able to instantly make the sense of the file size displayed using this command so why not alias `ls` command to always provide human readable file sizes. So here is my alias:
This is what I always want to see as the output with `ls` command. The same kind of alias can be used with `du` and `df` commands. There are number of other cases where aliasing a command with itself is good choice.
Another example is the less command. By default, you need to press q to exit less which can be quite annoying if the entire content can fit in a single screen. However, adding -F flag will gracefully quit after displaying the content if the content fits in a single screen. So I have my alias for less as below:
If something shoots in your mind, feel free to share here as a comment :)
Read more...
If you have been using linux shell for a while, I'm pretty sure you are now familiar with the `ls` command, if not I think you have just learnt to use man pages. Probably you've been using `ls -l` command to list files with the files size as well. Too bad, you won't just be able to instantly make the sense of the file size displayed using this command so why not alias `ls` command to always provide human readable file sizes. So here is my alias:
alias ls='ls -lh'
This is what I always want to see as the output with `ls` command. The same kind of alias can be used with `du` and `df` commands. There are number of other cases where aliasing a command with itself is good choice.
Another example is the less command. By default, you need to press q to exit less which can be quite annoying if the entire content can fit in a single screen. However, adding -F flag will gracefully quit after displaying the content if the content fits in a single screen. So I have my alias for less as below:
alias lesss='less -F'
If something shoots in your mind, feel free to share here as a comment :)
Read more...
Why Alias Command With Itself
2012-07-18T18:15:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|edubuntu|fedora|linux|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
edubuntu,
fedora,
linux,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Friday, 13 July 2012
Stack-based Directory Switching For Easy Reversal
So how many times have you used the `cd` command repeatedly to go back and forth of two or more directories. Probably you are already familiar to the `cd -` command which lets you switch between the current and the previous directory. But, many times this current and previous directory switching restriction will not suffice and hence a better option in such case is to use the `pushd` command instead of `cd`.
For example, just use the `pushd somedirA`, `pushd somedirB`, ... and like that. Now if you need to switch back, you can just use `popd` command and you'll be switching back easily. The `pushd` command saves the current directory path and then cds to the supplied path.
If you dig more, you'll come to know about the -n and -N switches you can combine with these commands so I will let you explore on this. Also, you can use the `dirs` command to view the stack of directories. If you are some computer student or enthusiast, you have already gotten an idea from a famous data structure called stack. Anyway, I hope this comes handy sometimes like it does to me :)
Read more...
For example, just use the `pushd somedirA`, `pushd somedirB`, ... and like that. Now if you need to switch back, you can just use `popd` command and you'll be switching back easily. The `pushd` command saves the current directory path and then cds to the supplied path.
If you dig more, you'll come to know about the -n and -N switches you can combine with these commands so I will let you explore on this. Also, you can use the `dirs` command to view the stack of directories. If you are some computer student or enthusiast, you have already gotten an idea from a famous data structure called stack. Anyway, I hope this comes handy sometimes like it does to me :)
Read more...
Stack-based Directory Switching For Easy Reversal
2012-07-13T12:20:00+05:45
Cool Samar
edubuntu|fedora|linux|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
edubuntu,
fedora,
linux,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Friday, 6 July 2012
Fix "trying to overwrite '*', which is also in package *"
Today I was updating few stuffs in edubuntu and dpkg was continually throwing me the problem while trying to install kdelibs-data. The error read as "trying to overwrite 'A', which is also in package X" and the fix was pretty straightforward but still I thought it would help someone out there.
Below is the exact error I was getting while trying to install kdelibs5-data from the deb file.
The fix was pretty simple. Add the --force-overwrite switch in the dpkg command as below:
I hope this comes useful sometimes.
Read more...
Below is the exact error I was getting while trying to install kdelibs5-data from the deb file.
dpkg: error processing /var/cache/apt/archives/
kdelibs5-data_4%3a4.4.5-0ubuntu1.2_all.deb (--unpack):
trying to overwrite '/usr/share/polkit-1/actions
/org.kde.kcontrol.kcmremotewidgets.policy', which is also in package kdebase-runtime-data 4:4.6.5-0ubuntu1
kdelibs5-data_4%3a4.4.5-0ubuntu1.2_all.deb (--unpack):
trying to overwrite '/usr/share/polkit-1/actions
/org.kde.kcontrol.kcmremotewidgets.policy', which is also in package kdebase-runtime-data 4:4.6.5-0ubuntu1
The fix was pretty simple. Add the --force-overwrite switch in the dpkg command as below:
dpkg -i --force-overwrite kdelibs5-data_4.4.5-0ubuntu1.2_all.deb
I hope this comes useful sometimes.
Read more...
Fix "trying to overwrite '*', which is also in package *"
2012-07-06T17:34:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|edubuntu|linux|ltsp|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
edubuntu,
linux,
ltsp,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Friday, 15 June 2012
Recover Deleted Files From An NTFS Volume Using Ntfsundelete
Ntfsundelete is a part of ntfsprogs, a suite of NTFS utilities based around a shared library. It lets us recover the deleted files from any NTFS volumes without making any changes in the NTFS volume itself.
Generally when a file is deleted from disks, it is some kind of pointer to the physical file that gets deleted and the actual content still remains in the disk unless it is overwritten by new files so it is possible to recover those files.
ntfsundelete has three modes of operation: scan, undelete and copy. By default, it will run in the scan mode which simply reads an NTFS volume and looks for the files that have been deleted.
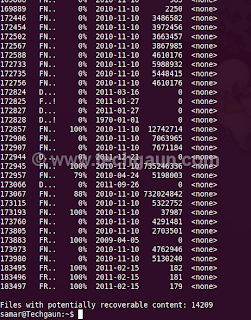
To use ntfsundelete, you'll have to install the ntfsprogs suite with following command in ubuntu and debian-based distros:
You'll have to first figure out which drive you want to recover. A handy command for this is:
Once you know the NTFS volume you want to recover, you can first run the scan mode to list the filenames that can be recovered.
The optional -f switch can be specified for the forceful scanning. There is a nice percentage field which gives the information on how much of the file can be recovered. You can apply the time and percentage filters to scan specific files. For example, you can use the following command to search for the files which can be recovered 100%
And, you can apply the time filter to list the files altered/deleted after the specified time. For example, following command will scan and list the files deleted in the last 14 days.
Other suffices you can use are d, w, m, y for days, weeks, months or years ago respectively.
Once you get the files to be recovered, you can use the -u switch to undelete or recover the files. An example of recovering files by pattern matching is as below:
Similarly you can recover by providing inode or inodes range using the -i switch. You can get the inode values from the first column in the scan mode.
Read more...
Generally when a file is deleted from disks, it is some kind of pointer to the physical file that gets deleted and the actual content still remains in the disk unless it is overwritten by new files so it is possible to recover those files.
ntfsundelete has three modes of operation: scan, undelete and copy. By default, it will run in the scan mode which simply reads an NTFS volume and looks for the files that have been deleted.

To use ntfsundelete, you'll have to install the ntfsprogs suite with following command in ubuntu and debian-based distros:
samar@Techgaun:~$ sudo apt-get install ntfsprogs
You'll have to first figure out which drive you want to recover. A handy command for this is:
samar@Techgaun:~$ sudo fdisk -l
Once you know the NTFS volume you want to recover, you can first run the scan mode to list the filenames that can be recovered.
samar@Techgaun:~$ sudo ntfsundelete /dev/sda4
The optional -f switch can be specified for the forceful scanning. There is a nice percentage field which gives the information on how much of the file can be recovered. You can apply the time and percentage filters to scan specific files. For example, you can use the following command to search for the files which can be recovered 100%
samar@Techgaun:~$ sudo ntfsundelete -p 100 /dev/sda4
And, you can apply the time filter to list the files altered/deleted after the specified time. For example, following command will scan and list the files deleted in the last 14 days.
samar@Techgaun:~$ sudo ntfsundelete -p 100 -t 2d /dev/sda4
Other suffices you can use are d, w, m, y for days, weeks, months or years ago respectively.
Once you get the files to be recovered, you can use the -u switch to undelete or recover the files. An example of recovering files by pattern matching is as below:
samar@Techgaun:~$ sudo ntfsundelete -u -m *.jpg /dev/sda4
Similarly you can recover by providing inode or inodes range using the -i switch. You can get the inode values from the first column in the scan mode.
samar@Techgaun:~$ sudo ntfsundelete -u -i 161922 /dev/sda4
Read more...
Recover Deleted Files From An NTFS Volume Using Ntfsundelete
2012-06-15T16:08:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|fedora|linux|ntfs|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
fedora,
linux,
ntfs,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Monday, 11 June 2012
Graphical Frontends To Sopcast Client For Linux
As all of you know the official Sopcast client for linux is only the command line version and many people find it difficult to use the CLI version. However, many good people have made an effort to write the graphical frontends to the Sopcast client for linux. Here you will find some of such GUI frontends for sopcast.
Sopcast Player: SopCast Player is designed to be an easy to use Linux GUI front-end for the p2p streaming technology developed by SopCast. SopCast Player features an integrated video player, a channel guide, and bookmarks. Once SopCast Player is installed it simply "just works" with no required configuration.
qsopcast: qsopcast is a QT GUI front-end of the Linux command line executive of P2P TV sopcast.
gsopcast: gsopcast is a GTK based GUI front-end for p2p TV sopcast.
TV-Maxe: TV-MAXE is an application which provides the ability to watch TV stations and listen radio via different streams, such is SopCast. Currently it has a large number of channels, both romanian and international.
SCPlayer: SCPlayer is a simple and lightweight GUI frontend for sopcast supporting only linux GNOME3 platform.
Pysopcast: It is a simple GUI for sopcast made using PyGTK.
totem-sopcast: A totem plugin to let you browse and play sopcast streams.
wxsopcast: A sopcast GUI for linux written in python and wxPython. Note that the channel URL needs to be changed to http://www.sopcast.com/gchlxml at first.
jsopcast: jsopcast is a simple GUI to see P2P TV sopcast made in Java.
If you know of any other GUI frontend for sopcast, please feel free to leave a comment. :)
Read more...
Sopcast Player: SopCast Player is designed to be an easy to use Linux GUI front-end for the p2p streaming technology developed by SopCast. SopCast Player features an integrated video player, a channel guide, and bookmarks. Once SopCast Player is installed it simply "just works" with no required configuration.
qsopcast: qsopcast is a QT GUI front-end of the Linux command line executive of P2P TV sopcast.
gsopcast: gsopcast is a GTK based GUI front-end for p2p TV sopcast.
TV-Maxe: TV-MAXE is an application which provides the ability to watch TV stations and listen radio via different streams, such is SopCast. Currently it has a large number of channels, both romanian and international.
SCPlayer: SCPlayer is a simple and lightweight GUI frontend for sopcast supporting only linux GNOME3 platform.
Pysopcast: It is a simple GUI for sopcast made using PyGTK.
totem-sopcast: A totem plugin to let you browse and play sopcast streams.
wxsopcast: A sopcast GUI for linux written in python and wxPython. Note that the channel URL needs to be changed to http://www.sopcast.com/gchlxml at first.
jsopcast: jsopcast is a simple GUI to see P2P TV sopcast made in Java.
If you know of any other GUI frontend for sopcast, please feel free to leave a comment. :)
Read more...
Graphical Frontends To Sopcast Client For Linux
2012-06-11T01:04:00+05:45
Cool Samar
fedora|linux|sopcast|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
fedora,
linux,
sopcast,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Sunday, 10 June 2012
Sopcast Player With GUI In Linux
SopCast is a simple, free way to broadcast video and audio or watch the video and listen to radio on the Internet. Adopting P2P(Peer-to-Peer) technology, It is very efficient and easy to use. The GUI for sopcast player for linux works pretty well and this post gives you the step by step process of installation of sopcast player in linux.
Follow the steps as below for easy installation under ubuntu. Instructions should be similar in many variants:

Now everything should work fine. I hope this helps. :)
Read more...
Follow the steps as below for easy installation under ubuntu. Instructions should be similar in many variants:
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop$ su
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/# mkdir sopcast && cd sopcast/
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# wget http://www.sopcast.com/download/libstdcpp5.tgz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# wget http://sopcast-player.googlecode.com/files/sp-auth-3.2.6.tar.gz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# wget http://sopcast-player.googlecode.com/files/sopcast-player-0.8.5.tar.gz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# tar -xvf sopcast-player-0.8.5.tar.gz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# tar -xvf sp-auth-3.2.6.tar.gz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# tar -xvf libstdcpp5.tgz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# apt-get install gettext python-setuptools libvlc-dev
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# cd sopcast-player
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# make
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# make install
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# cd ../sp-auth
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast/sp-auth# cp sp-sc-auth /usr/bin/
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# cd ../usr/lib/
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast/usr/lib/# cp -a libstdc++.so.5* /usr/lib/
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast/usr/lib/# sopcast-player
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/# mkdir sopcast && cd sopcast/
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# wget http://www.sopcast.com/download/libstdcpp5.tgz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# wget http://sopcast-player.googlecode.com/files/sp-auth-3.2.6.tar.gz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# wget http://sopcast-player.googlecode.com/files/sopcast-player-0.8.5.tar.gz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# tar -xvf sopcast-player-0.8.5.tar.gz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# tar -xvf sp-auth-3.2.6.tar.gz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# tar -xvf libstdcpp5.tgz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# apt-get install gettext python-setuptools libvlc-dev
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# cd sopcast-player
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# make
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# make install
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# cd ../sp-auth
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast/sp-auth# cp sp-sc-auth /usr/bin/
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# cd ../usr/lib/
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast/usr/lib/# cp -a libstdc++.so.5* /usr/lib/
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast/usr/lib/# sopcast-player

Now everything should work fine. I hope this helps. :)
Read more...
Sopcast Player With GUI In Linux
2012-06-10T23:46:00+05:45
Cool Samar
linux|sopcast|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
linux,
sopcast,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Friday, 8 June 2012
Now NTC Hosts Ubuntu Repository For Nepal
As most of the ubuntu users know that the previous nepali repository hosted by Mitra Network Pvt. Ltd. had lots of problem in packages and later went down for a long time. This time, it is NTC who has taken a good initiative and has started providing local ubuntu repository for us.
As seen on foss nepal's mailing list, everybody seems to be happy with the effort of NTC to promote linux and open source software tools in Nepal.
The np.archive.ubuntu.com is now resolving to ubuntu.ntc.net.np now. You can edit your sources.list and choose the nepali repository now. :)
Also, lots of ubuntu distros are available for download. See THIS. Now I can download ubuntu ISO's in around one or two minutes(Thanks NPIX for keeping local traffic local)
In case anyone wants my copy of sources.list file, here it is: sources.list or get it from HERE in case you hate registering on 4shared.
Once you copy the sources.list to /etc/apt/sources.list, make sure to run sudo apt-get update to update the package database.
Read more...
As seen on foss nepal's mailing list, everybody seems to be happy with the effort of NTC to promote linux and open source software tools in Nepal.
The np.archive.ubuntu.com is now resolving to ubuntu.ntc.net.np now. You can edit your sources.list and choose the nepali repository now. :)
Also, lots of ubuntu distros are available for download. See THIS. Now I can download ubuntu ISO's in around one or two minutes(Thanks NPIX for keeping local traffic local)
In case anyone wants my copy of sources.list file, here it is: sources.list or get it from HERE in case you hate registering on 4shared.
Once you copy the sources.list to /etc/apt/sources.list, make sure to run sudo apt-get update to update the package database.
Read more...
Now NTC Hosts Ubuntu Repository For Nepal
2012-06-08T21:49:00+05:45
Cool Samar
news|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
news,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Sunday, 27 May 2012
Accelerate Download Speed In Linux Using Axel
Axel is a lightweight command line download accelerator for linux. Axel is a program that downloads a file from a FTP or HTTP server through multiple connection, each connection downloads its own part of the file.
Unlike most other programs, Axel downloads all the data directly to the destination file, using one single thread. It just saves some time at the end because the program doesn't have to concatenate all the downloaded parts.
Axel tries to accelerate downloads by using multiple connections (possibly to multiple servers) for one download. Because of its size, it might be very useful on bootdisks or other small systems as a wget replacement.
One useful implementation of axel is in the apt-fast tool, a fusion of apt-get and axel to accelerate downloads of packages.
Installation under ubuntu and other debian distros: Open the terminal and type:
Similarly, a graphical frontend axel-kapt is also available for download for GUI lovers. Also, flashgot plugin for firefox lets you make use of axel to download files. I should say, axel is a small yet good download accelerator for linux systems.
Read more...
Unlike most other programs, Axel downloads all the data directly to the destination file, using one single thread. It just saves some time at the end because the program doesn't have to concatenate all the downloaded parts.
Axel tries to accelerate downloads by using multiple connections (possibly to multiple servers) for one download. Because of its size, it might be very useful on bootdisks or other small systems as a wget replacement.
One useful implementation of axel is in the apt-fast tool, a fusion of apt-get and axel to accelerate downloads of packages.
Installation under ubuntu and other debian distros: Open the terminal and type:
sudo apt-get install axel
Similarly, a graphical frontend axel-kapt is also available for download for GUI lovers. Also, flashgot plugin for firefox lets you make use of axel to download files. I should say, axel is a small yet good download accelerator for linux systems.
Read more...
Accelerate Download Speed In Linux Using Axel
2012-05-27T21:38:00+05:45
Cool Samar
axel|command line|download|linux|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
axel,
command line,
download,
linux,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)


