Showing posts with label command line. Show all posts
Showing posts with label command line. Show all posts
Sunday, 10 November 2013
JPEG To PDF With Imagemagick
ImageMagick is an awesome toolkit with several powerful features for image creation and manipulation. You can use ImageMagick to translate, flip, mirror, rotate, scale, shear and transform images, adjust image colors, apply various special effects, or draw text, lines, polygons, ellipses and Bezier curves. Here, I will show how you can use ImageMagick suite to convert JPEG to PDF quickly.
First make sure imagemagick suite is installed in your system.
Ubuntu/Debian
CentOS/Fedora
Below are some of the examples of using convert which is a part of ImageMagick to convert Jpeg to PDF.
Single Image
Multiple Images
Resize and Convert
Negate and Convert
You can actually use different available switches to get your output as expected. I usually use PdfTk in conjunction with this technique to work in different scenarios and it really works great. I hope this helps :)
Read more...
First make sure imagemagick suite is installed in your system.
Ubuntu/Debian
$ sudo apt-get install imagemagick
CentOS/Fedora
$ sudo yum install imagemagick
Below are some of the examples of using convert which is a part of ImageMagick to convert Jpeg to PDF.
Single Image
$ convert image.jpg image.pdf
Multiple Images
$ convert 1.jpg 2.jpg 3.jpg output.pdf
Resize and Convert
$ convert -resize 80% image.jpg image.pdf
Negate and Convert
$ convert -negate image.jpg image.pdf
You can actually use different available switches to get your output as expected. I usually use PdfTk in conjunction with this technique to work in different scenarios and it really works great. I hope this helps :)
Read more...
JPEG To PDF With Imagemagick
2013-11-10T16:40:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|imagemagick|linux|pdf|pdf tool|pdftk|tricks and tips|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
imagemagick,
linux,
pdf,
pdf tool,
pdftk,
tricks and tips
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Wednesday, 30 January 2013
Search Text Over Multiple PDF Files In Linux
You can use the old grep command or the small script using the pdftotext command to search text over multiple pdf files but we are talking about a simple utility that lets us to search text in PDF files.
The pdfgrep tool lets you perform grep style search over multiple pdf files easily from the terminal. It depends upon the poppler package and under ubuntu, you can just type the command below to install pdfgrep.
Once pdfgrep is installed, you can perform any kind of search like you would do while using the grep command. Enjoy grepping the PDF files :)
Read more...
The pdfgrep tool lets you perform grep style search over multiple pdf files easily from the terminal. It depends upon the poppler package and under ubuntu, you can just type the command below to install pdfgrep.
samar@\Techgaun:~$ sudo apt-get install pdfgrep
Once pdfgrep is installed, you can perform any kind of search like you would do while using the grep command. Enjoy grepping the PDF files :)
Read more...
Search Text Over Multiple PDF Files In Linux
2013-01-30T23:05:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|linux|pdf|tricks and tips|ubuntu|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
linux,
pdf,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Tuesday, 29 January 2013
Swasthani.com Swasthani Ripper
Yesterday I came to know that I can listen Swasthani online at this site, www.swasthani.com and I decided to write a swasthani audio downloader. Since it would be useful for everyone, here is the script.
From the site itself, Sri Swasthani Brata Katha is a very popular ritual observed in Nepal in the Poush month (January – February) during winter. Goddess Sri Swasthani, known to grant wishes of her devotees, is worshipped for the whole month of Poush. The Swasthani Brat Katha (story) is recited everyday. The month long telling of the tales are dedicated to the Goddess and the stories that are mainly narrated are those of Swasthani Devi, Lord Shiva and other Gods.
Save the above file as swasthani, then chmod for executable permission and run it. If you have problem copying above code, you can check the Swasthani Downloader at GitHub. Enjoy listening Swasthani, geeks :)
Read more...
From the site itself, Sri Swasthani Brata Katha is a very popular ritual observed in Nepal in the Poush month (January – February) during winter. Goddess Sri Swasthani, known to grant wishes of her devotees, is worshipped for the whole month of Poush. The Swasthani Brat Katha (story) is recited everyday. The month long telling of the tales are dedicated to the Goddess and the stories that are mainly narrated are those of Swasthani Devi, Lord Shiva and other Gods.
#!/bin/bash ############################################### # Swasthani.com Swasthani Ripper # # Samar @ http://www.techgaun.com # ############################################### if [[ ! -f /tmp/swasthani.txt ]] then wget http://www.swasthani.com/ -O - | egrep '<li class="leaf( first| last)?"><a href="/swasthani/' | grep -o '<a .*href=.*>' | sed -e 's/<a /\n<a /g' | sed -e 's/<a .*href=['"'"'"]//' -e 's/["'"'"'].*$//' -e '/^$/ d' > /tmp/swasthani.txt fi while read -r line do wget "http://www.swasthani.com$line" -O - | egrep 'data="soundFile=http://www.swasthani.com/system/files/' | cut -d\" -f6 | cut -d= -f2 | wget -nc -i - done </tmp/swasthani.txt
Save the above file as swasthani, then chmod for executable permission and run it. If you have problem copying above code, you can check the Swasthani Downloader at GitHub. Enjoy listening Swasthani, geeks :)
Read more...
Swasthani.com Swasthani Ripper
2013-01-29T20:00:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|linux|new release|swasthani|ubuntu|web|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
linux,
new release,
swasthani,
ubuntu,
web
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
How To Check Which Groups You Belong To
In this post, you will get to know about a simple command that lets you know what groups the particular user belongs to. Users and groups are the one of the several concepts employed in the Linux systems for access control.
From the man page, the groups command does is:
Print group memberships for each USERNAME or, if no USERNAME is specified, for the current process (which may differ if the groups database has changed).
So if you are interested in finding what group a particular user is in, run the command as below. Replace samar with your USERNAME and you are good to go:
I hope this proves useful :)
Read more...
From the man page, the groups command does is:
Print group memberships for each USERNAME or, if no USERNAME is specified, for the current process (which may differ if the groups database has changed).
So if you are interested in finding what group a particular user is in, run the command as below. Replace samar with your USERNAME and you are good to go:
samar@Techgaun:~$ groups samar
samar : samar adm cdrom sudo vboxusers ....
samar : samar adm cdrom sudo vboxusers ....
I hope this proves useful :)
Read more...
How To Check Which Groups You Belong To
2013-01-29T18:55:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|linux|linuxmint|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
linux,
linuxmint,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Saturday, 27 October 2012
Accelerate Your Softwares Update Speed Using Apt-fast
Long ago, I had posted about apt-fast script which used axel to create multiple HTTP connections and increase the download speed of software updates and packages. In this post, you will get the details for installing apt-fast from PPA.
apt-fast is a shellscript wrapper for apt-get and aptitude that can drastically improve apt download times by downloading packages in parallel, with multiple connections per package.
As a pre-requisite, we will first install axel, a simple yet very useful command line download accelerator. Alternatively, you can also use aria accelerator with apt-fast.
Then you will have to add a PPA for apt-fast, update the database, and install apt-fast.
You need to configure few options afterwards as below:
For manual installation and grabbing the source code, check the GitHub.
Once you install apt-fast, you can install softwares and perform updates from the repos using the command below:
I hope this becomes useful :)
Read more...
As a pre-requisite, we will first install axel, a simple yet very useful command line download accelerator. Alternatively, you can also use aria accelerator with apt-fast.
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ sudo apt-get install axel
Then you will have to add a PPA for apt-fast, update the database, and install apt-fast.
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:apt-fast/stable samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ sudo apt-get update samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ sudo apt-get install apt-fast
You need to configure few options afterwards as below:
For manual installation and grabbing the source code, check the GitHub.
Once you install apt-fast, you can install softwares and perform updates from the repos using the command below:
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ sudo apt-fast install package_name
I hope this becomes useful :)
Read more...
Accelerate Your Softwares Update Speed Using Apt-fast
2012-10-27T17:26:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|download|edubuntu|ubuntu|ubuntu 12.04|ubuntu 12.10|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
download,
edubuntu,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 12.04,
ubuntu 12.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Linux Cat Command Examples
The cat command displays the content of file on the standard output. If multiple files are specified, the contents of all files will be concatenated and then displayed on the standard output. Likewise, if no file is specified, it will assume standard input (keyboard input) as the input to the command. The Ctrl + d is the shortcut used to save the contents in the appropriate output placeholder specified and exit the cat command.
Print content of file in standard output
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat workers.txt List of workers, designations & salary (in K): Kshitiz Director 30 Bikky Manager 20 Abhis Sweeper 10 Rajesh Guard 12
Print line numbers
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat -n workers.txt
1 List of workers, designations & salary (in K):
2 Kshitiz Director 30
3 Bikky Manager 20
4
5
6 Abhis Sweeper 10
7 Rajesh Guard 12
Print line numbers for non-empty lines only
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat -b workers.txt
1 List of workers, designations & salary (in K):
2 Kshitiz Director 30
3 Bikky Manager 20
4 Abhis Sweeper 10
5 Rajesh Guard 12
Create a new file
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat > newfile.txt We can create text files using cat command once u finish writing, press ctrl+d to save file ^d
Display content of multiple files
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat workers.txt newfile.txt List of workers, designations & salary (in K): Kshitiz Director 30 Bikky Manager 20 Abhis Sweeper 10 Rajesh Guard 12 We can create text files using cat command once u finish writing, press ctrl+d to save file
Combine multiple files to new file
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat workers.txt newfile.txt > concat.txt samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat concat.txt List of workers, designations & salary (in K): Kshitiz Director 30 Bikky Manager 20 Abhis Sweeper 10 Rajesh Guard 12 We can create text files using cat command once u finish writing, press ctrl+d to save file
Append data to existing file
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat >> newfile.txt New line added ^d samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat newfile.txt We can create text files using cat command once u finish writing, press ctrl+d to save file New line added
Alternatively, you can use the syntax below if you wish to create new file combining the content of already existing file and standard input.
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat newfile.txt - > myfile thanks for everything ^d samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat myfile We can create text files using cat command once u finish writing, press ctrl+d to save file New line added thanks for everything
Another possibility is to combine two text files with data from standard input (keyboard) in-between the contents of these two text files.
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat workers.txt - newfile.txt > myfile ---------------------------------- ^d samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat myfile List of workers, designations & salary (in K): Kshitiz Director 30 Bikky Manager 20 Abhis Sweeper 10 Rajesh Guard 12 ---------------------------------- We can create text files using cat command once u finish writing, press ctrl+d to save file New line added
Display $ sign at the end of each line
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat -E workers.txt List of workers, designations & salary (in K):$ Kshitiz Director 30$ Bikky Manager 20$ $ $ Abhis Sweeper 10$ Rajesh Guard 12$
Display ^I sign instead of TABs
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat -T workers.txt List of workers, designations & salary (in K): Kshitiz^IDirector^I30 Bikky^IManager^I^I20 Abhis^ISweeper^I^I10 Rajesh^IGuard^I^I12
Display files with non-printing characters
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat -v /bin/nc
In the example above, the non-printing characters are replaced with ^ and M- notation except for line breaks and TABs. This can be used to display the contents of binary files which would otherwise have shown gibberish text all over the console.
Show contents with tabs, line breaks and non-printing characters
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat -A /bin/nc
The tab will be substituted by ^I, line breaks with $ and non-printing characters with ^ and M- notation. Actually, the -A switch is equivalent to -vET switch.
Supress/squeeze repeated empty lines
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat -s workers.txt List of workers, designations & salary (in K): Kshitiz Director 30 Bikky Manager 20 Abhis Sweeper 10 Rajesh Guard 12
Using -s switch, we can squeeze repeatedly occurring blank lines and replace all the adjacent empty lines with a single empty line in the output. This might be useful to reformat a file with several empty lines in-between (eg. cat -s workers.txt > formatted_workers.txt).
Display last line first
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ tac workers.txt Rajesh Guard 12 Abhis Sweeper 10 Bikky Manager 20 Kshitiz Director 30 List of workers, designations & salary (in K):
It is the tac, not the cat that is doing the magic but just thought that this is the right place to make a note about this little known command.
Edit: Added here-doc examples. Thanks rho dai for pointing me this.
Parameter substitution using here-document strings
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat > test << TEST samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ I am $USER. My home is $HOME samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ I came here from $OLDPWD samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ TEST samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat test I am samar. My home is /home/samar I came here from /home/samar/Downloads
Command expansion example
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat > test << TEST samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ $(ls /) samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ TEST samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat test bin boot cdrom dev etc home initrd.img initrd.img.old lib lost+found media mnt opt proc root run sbin selinux srv sys tmp usr var vmlinuz vmlinuz.old
Parameter substitution turned off
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat > test << 'TEST' samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ I am $USER. My home is $HOME samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ I came here from $OLDPWD samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ TEST samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cat test I am $USER. My home is $HOME I came here from $OLDPWD
Note the difference between the last example and previous two examples. Enclosing the limit string TEST with quotes prevents the substitutions and expansions.
I hope these examples are useful. :)
Read more...
Linux Cat Command Examples
2012-10-27T14:17:00+05:45
Cool Samar
bash|command line|fedora|linux|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|ubuntu 12.04|ubuntu 12.10|unix|
Comments
Labels:
bash,
command line,
fedora,
linux,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10,
ubuntu 12.04,
ubuntu 12.10,
unix
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Sunday, 21 October 2012
Enable Auto Correction Of Path In Bash
While using the cd command, its normal to make mistakes while typing the directory path. You can enable auto-correction while typing directory path by enabling a particular shell option.
Minor spelling mistakes will be corrected automatically if the particular shell option cdspell using the SHell OPTions command invoked with shopt command.
When you enable the cdspell shell option, the errors checked for are missing characters, repeated characters, and transposed characters. Once the error is encountered, the corrected path is printed and directory is changed successfully.
The line shopt -s cdspell enables the auto-correction while using cd command. The session above shows some of the corrections performed once we enabled the cdspell shell option.
If you want to turn on this particular setting, then add the appropriate line using the command below:
I hope this counts as useful tips to beginner linux guys ;)
Read more...
Minor spelling mistakes will be corrected automatically if the particular shell option cdspell using the SHell OPTions command invoked with shopt command.
When you enable the cdspell shell option, the errors checked for are missing characters, repeated characters, and transposed characters. Once the error is encountered, the corrected path is printed and directory is changed successfully.
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ shopt -s cdspell
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cd Desktp
Desktop
samar@samar-Techgaun:~/Desktop$ cd ../Deskotp/
../Desktop/
samar@samar-Techgaun:~/Desktop$ cd ../Desktoop
../Desktop
samar@samar-Techgaun:~/Desktop$
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ cd Desktp
Desktop
samar@samar-Techgaun:~/Desktop$ cd ../Deskotp/
../Desktop/
samar@samar-Techgaun:~/Desktop$ cd ../Desktoop
../Desktop
samar@samar-Techgaun:~/Desktop$
The line shopt -s cdspell enables the auto-correction while using cd command. The session above shows some of the corrections performed once we enabled the cdspell shell option.
If you want to turn on this particular setting, then add the appropriate line using the command below:
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "shopt -s cdspell" >> ~/.bash_profile
I hope this counts as useful tips to beginner linux guys ;)
Read more...
Enable Auto Correction Of Path In Bash
2012-10-21T17:05:00+05:45
Cool Samar
bash|command line|tricks and tips|ubuntu|
Comments
Labels:
bash,
command line,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Tuesday, 16 October 2012
Practical ls Command Examples For Fun & Profit
The power of linux lies in the shell through which we can perform complex job in no time. While the directory listing command 'ls' seems to be very simple command, the linux shell provides the power to use switches and pipes to do anything from terminal. Check out this list with practically useful examples using ls.
Any more example that fires up in your mind? Feel free to share over here ;)
Read more...
Display all files including hidden files/folders
ls -a
Display one file/folder per line
ls -1
Count number of files & folders
ls -1 | wc -l
Human readable file sizes (eg. Mb or Gb)
ls -lh
Alphabetically sort the listing
ls -X
Only list the folders in current directory
ls -d */
ls -p | grep /
ls -p | grep /
Display folders in current directory consisting certain patterns
ls -l D* | grep :$
ls -l *a* | grep :$
ls -l *a* | grep :$
List files by descending order of modification time
ls -lt
ls -l --sort=time #alternative long version
ls -l --sort=time #alternative long version
List files by descending order of creation time
ls -lct
List files in reverse order
ls -ltr
ls -l --sort=time --reverse #alternative long version
ls -l --sort=time --reverse #alternative long version
List files in descending order of file size
ls -lSh
ls -lh --sort=size
ls -lSh1 *.avi #find largest AVI file
rm `ls -S1 | head -1` #delete largest file in current folder
ls -lh --sort=size
ls -lSh1 *.avi #find largest AVI file
rm `ls -S1 | head -1` #delete largest file in current folder
List files in ascending order of file size
ls -lShr
ls -lh --sort=size --reverse #alternative long version
ls -lh --sort=size --reverse #alternative long version
Display directories in recursive manner
ls -R
Display the files/folders created today
ls -l --time-style=+%F | grep `date +%F`
Display the files/folders created this year
ls -l --time-style=+%y | grep `date +%y`
Any more example that fires up in your mind? Feel free to share over here ;)
Read more...
Practical ls Command Examples For Fun & Profit
2012-10-16T00:44:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|edubuntu|fedora|linux|ubuntu|ubuntu 12.04|ubuntu 12.10|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
edubuntu,
fedora,
linux,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 12.04,
ubuntu 12.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Saturday, 13 October 2012
How To Exclude Directory While Compressing With Tar
Quite a handy and useful tip here. Several times, you want to compress files and folders but there might be cases when you want to compress your data excluding some of the directories. Tar command makes the process easier by providing us a exclusion switch.
I was actually backing up data I had downloaded in the remote server and wanted a copy of backup tar file in my system as well. But all those images that resided in the folders deep inside were not necessary for me. So all I did was something like below:
The above command effectively excludes all the sub directories from testdirectory having the string image (eg. image, images, images_old in my case) and creates the backup.tar file. Moreover, the --exclude switch also co-operates the regular expressions so you can specify the regex to filter the directories. As an example, the command below excludes the directories a, b, c, d, and e while creating the tarball.
You can exploit this switch for ease several times in your daily works. I hope this helps :)
Read more...
I was actually backing up data I had downloaded in the remote server and wanted a copy of backup tar file in my system as well. But all those images that resided in the folders deep inside were not necessary for me. So all I did was something like below:
adm@RServ:~$ tar cvf backup.tar test --exclude=image*
The above command effectively excludes all the sub directories from testdirectory having the string image (eg. image, images, images_old in my case) and creates the backup.tar file. Moreover, the --exclude switch also co-operates the regular expressions so you can specify the regex to filter the directories. As an example, the command below excludes the directories a, b, c, d, and e while creating the tarball.
adm@RServ:~$ tar cvf backup.tar test --exclude=[a-e]
You can exploit this switch for ease several times in your daily works. I hope this helps :)
Read more...
How To Exclude Directory While Compressing With Tar
2012-10-13T19:32:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|linux|tricks and tips|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
linux,
tricks and tips
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Empty Trash From Command Line In Ubuntu
CLI is such a sexy piece so why bother using GUI, even for cleaning up your trash. In this post, you will see how you can empty trash in Ubuntu from command line.
The trash you see in GUI is nothing but just the view for the files deleted by users which are temporarily moved to the special location of user's home directory. For any user, the trash location is ~/.local/share/Trash/. That is, whatever a user deletes gets saved in this location.
I hope this becomes useful :)
Read more...
The trash you see in GUI is nothing but just the view for the files deleted by users which are temporarily moved to the special location of user's home directory. For any user, the trash location is ~/.local/share/Trash/. That is, whatever a user deletes gets saved in this location.
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ rm -rf ~/.local/share/Trash/
I hope this becomes useful :)
Read more...
Empty Trash From Command Line In Ubuntu
2012-10-13T16:11:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|ubuntu 12.04|ubuntu 12.10|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10,
ubuntu 12.04,
ubuntu 12.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Add Google Search Support In Gnome-Terminal
Gnome-terminal is my favorite thing in my system and recently I came to know that I could add google search support in gnome-terminal which is totally awesome. Ubuntu Tweak already includes the google search support but if you want google search in your terminal without the whole ubuntu tweak, you can follow this guide.
All you need to do is add the PPA and you can easily install the gnome-terminal with google search support. Fire up the terminal and enter the following commands:
Credits: Ubuntu Tweak
Read more...
All you need to do is add the PPA and you can easily install the gnome-terminal with google search support. Fire up the terminal and enter the following commands:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:tualatrix/personal
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install gnome-terminal
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install gnome-terminal
Credits: Ubuntu Tweak
Read more...
Add Google Search Support In Gnome-Terminal
2012-10-13T09:22:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|tricks and tips|ubuntu|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Tuesday, 2 October 2012
Binary, Hex, Octal and Decimal Conversion Under Linux
Base conversions are easy with linux CLI. No need of fancy GUI-based calculator to perform base conversions when there is our favorite linux terminal.
We will be using bc, a calculator language that supports arbitrary precision numbers with interactive execution of statements. We will exploit the pipelining feature of shell and will let the bc process our query to convert the numbers from one base to other.
As seen in all the examples above, the conversion to decimal numbers does not require you to specify the obase as obase defaults to decimal. The same thing applies for ibase i.e. ibase defaults to decimal base by default as seen in the examples below.
Now lets try some conversion with decimal numbers as the input base.
Below are few more examples of base conversions to clarify the use of the command.
I hope this is helpful ;-)
Read more...
We will be using bc, a calculator language that supports arbitrary precision numbers with interactive execution of statements. We will exploit the pipelining feature of shell and will let the bc process our query to convert the numbers from one base to other.
From binary to decimal
The syntax is obvious and we will follow the similar syntax for all the conversions. In this first example, we are converting the binary number 1101101 from input base binary to decimal(obase defaults to decimal unless specified).
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "ibase=2;1101101" | bc
109
109
From octal to decimal
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "ibase=8;1101101" | bc
295489
295489
From Hexadecimal to decimal
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "ibase=16;A1F3DF" | bc
10613727
10613727
From N-base to decimal
All you need to do is provide the appropriate ibase value (eg. ibase=4 for 4-base to decimal conversion).
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "ibase=16;A1F3DF" | bc
10613727
10613727
As seen in all the examples above, the conversion to decimal numbers does not require you to specify the obase as obase defaults to decimal. The same thing applies for ibase i.e. ibase defaults to decimal base by default as seen in the examples below.
Now lets try some conversion with decimal numbers as the input base.
From decimal to binary
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "obase=2;109" | bc
1101101
1101101
From decimal to octal
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "obase=8;295489" | bc
1101101
1101101
From decimal to hexadecimal
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "obase=16;10613727" | bc
A1F3DF
A1F3DF
From decimal to N-base
All you need to do is provide the appropriate obase value (eg. obase=4 for decimal to 4-base conversion).
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "obase=4;121" | bc
1321
1321
Below are few more examples of base conversions to clarify the use of the command.
From binary to octal
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "ibase=2;obase=8;1111" | bc
17
17
From hexadecimal to binary
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "ibase=16;obase=2;AFBE" | bc
1010111110111110
1010111110111110
I hope this is helpful ;-)
Read more...
Binary, Hex, Octal and Decimal Conversion Under Linux
2012-10-02T22:12:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|linux|mathematics|tricks and tips|ubuntu|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
linux,
mathematics,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Friday, 14 September 2012
How To Find The Location Of Command In Linux
Sometimes you need to find the pathnames or locations of commands you use frequently. In this post, I am going to discuss two useful commands that are useful for locating Linux commands.
The first command to locate the Linux commands is which. This command returns the pathnames of the files or links. However, it does not follow the symbolic links.
You can also find the pathnames of multiple commands at once using which command.
The other command is type command which is useful to determine if a command is an alias, a built-in command or an independent command.
You can play more with the type command. I hope this helps :)
Read more...
The first command to locate the Linux commands is which. This command returns the pathnames of the files or links. However, it does not follow the symbolic links.
samar@Techgaun:~$ which bash
/bin/bash
/bin/bash
You can also find the pathnames of multiple commands at once using which command.
samar@Techgaun:~$ which -a bash cat ls iftop
/bin/bash
/bin/cat
/bin/ls
/usr/sbin/iftop
/bin/bash
/bin/cat
/bin/ls
/usr/sbin/iftop
The other command is type command which is useful to determine if a command is an alias, a built-in command or an independent command.
samar@Techgaun:~$ type gedit
gedit is /usr/bin/gedit
samar@Techgaun:~$ type grep
grep is aliased to `grep --color=auto'
samar@Techgaun:~$ type -t iftop
file
gedit is /usr/bin/gedit
samar@Techgaun:~$ type grep
grep is aliased to `grep --color=auto'
samar@Techgaun:~$ type -t iftop
file
You can play more with the type command. I hope this helps :)
Read more...
How To Find The Location Of Command In Linux
2012-09-14T01:05:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|linux|ubuntu|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
linux,
ubuntu
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Monday, 3 September 2012
Preventing Accidental Overwriting Of Files In Bash Shell
How many times has this happened to you? It used to happen once in a while with me. A Linux user learns to use the redirection operators such as '>' and '>>' but accidental overwriting starts to become common in commands you use and shell scripts you write.
The accidental overwriting of files that happens unintentionally is known as clobbering and it commonly happens while using the '>' redirection operator.
In the above example, the mycmd clobbers any existing data in the myfile file if that file exists already. Worse things may happen sometime. Imagine accidentally typing
instead of possibly using other redirection operators (like >> or <). Thankfully, you could recover /etc/passwd from either /etc/passwd- or /var/backups/passwd.bak if you hadn't rm'd these files.
To prevent such accidental overwriting, we can set the noclobber environment variable. Below is a session of enabling this variable:
As seen above, you have to turn on the noclobber variable using the set -o noclobber command in your shell. However, you might want to intentionally overwrite contents of certain files even when the noclobber is turned on.
Notice the >| in place of your normal > redirection operator. Using this operator, you can however overwrite the existing files even if the noclobber is turned on.
If you want to turn off the noclobber variable, type the following:
You can also permanently turn on the noclobber by the following command:
Moreover, such accidental overwriting can be prevented by enabling the interactive mode which is available in most of the linux commands. For example, you can write the alias for many commands that are likely to cause accidental overwriting. See some examples of aliases below:
You could even keep these aliases in your ~/.bashrc file permanently. Enabling such interactive modes by default in the commands that are more likely to cause accidental overwriting can prevent clobbering in many cases.
I hope this proves useful to you :)
Read more...
The accidental overwriting of files that happens unintentionally is known as clobbering and it commonly happens while using the '>' redirection operator.
samar@Techgaun:~$ mycmd > myfile
In the above example, the mycmd clobbers any existing data in the myfile file if that file exists already. Worse things may happen sometime. Imagine accidentally typing
samar@Techgaun:~$ mycmd > /etc/passwd
instead of possibly using other redirection operators (like >> or <). Thankfully, you could recover /etc/passwd from either /etc/passwd- or /var/backups/passwd.bak if you hadn't rm'd these files.
To prevent such accidental overwriting, we can set the noclobber environment variable. Below is a session of enabling this variable:
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ echo "www.techgaun.com" > myfile
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ echo "Overwriting techgaun.com" > myfile
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ set -o noclobber
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ echo "Retrying to overwrite" > myfile
-bash: myfile: cannot overwrite existing file
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ echo "Overwriting techgaun.com" > myfile
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ set -o noclobber
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ echo "Retrying to overwrite" > myfile
-bash: myfile: cannot overwrite existing file
As seen above, you have to turn on the noclobber variable using the set -o noclobber command in your shell. However, you might want to intentionally overwrite contents of certain files even when the noclobber is turned on.
samar@Techgaun:~$ mycmd >| myfile
Notice the >| in place of your normal > redirection operator. Using this operator, you can however overwrite the existing files even if the noclobber is turned on.
If you want to turn off the noclobber variable, type the following:
samar@Techgaun:~$ set +o noclobber
You can also permanently turn on the noclobber by the following command:
samar@Techgaun:~$ echo "set -o noclobber" >> ~/.bashrc
Moreover, such accidental overwriting can be prevented by enabling the interactive mode which is available in most of the linux commands. For example, you can write the alias for many commands that are likely to cause accidental overwriting. See some examples of aliases below:
samar@Techgaun:~$ alias rm=rm -i
samar@Techgaun:~$ alias mv=mv -i
samar@Techgaun:~$ alias mv=mv -i
You could even keep these aliases in your ~/.bashrc file permanently. Enabling such interactive modes by default in the commands that are more likely to cause accidental overwriting can prevent clobbering in many cases.
I hope this proves useful to you :)
Read more...
Preventing Accidental Overwriting Of Files In Bash Shell
2012-09-03T22:56:00+05:45
Cool Samar
bash|command line|fedora|filesystem|linux|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
bash,
command line,
fedora,
filesystem,
linux,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Sunday, 2 September 2012
How To Search Manual Pages In Linux
Linux system consists of hundreds of binaries, several syscalls, and other stuffs that do have manual page. What if you want to locate or find the commands by searching through the manual pages? In this post, I am going to talk about one such useful command to search through the manual page names and short descriptions.
The command I am talking about is the apropos command. The best way to learn any linux command is to read its corresponding manual and go through the help (-h or --help) so lets poke through the help of apropos itself.
Particularly, the -e switch is quite useful to filter out your search. See the example below:
Each command has its associated short description and the apropos command searches the short description section of appropriate manual page for the provided keyword. You can also specify the search keywords in the form of regular expression for more flexibility. I hope this command counts as useful one :)
Read more...
The command I am talking about is the apropos command. The best way to learn any linux command is to read its corresponding manual and go through the help (-h or --help) so lets poke through the help of apropos itself.
samar@Techgaun:~$ apropos -h
Usage: apropos [OPTION...] KEYWORD...
-d, --debug emit debugging messages
-v, --verbose print verbose warning messages
-e, --exact search each keyword for exact match
-r, --regex interpret each keyword as a regex
-w, --wildcard the keyword(s) contain wildcards
-a, --and require all keywords to match
-l, --long do not trim output to terminal width
-C, --config-file=FILE use this user configuration file
-L, --locale=LOCALE define the locale for this search
-m, --systems=SYSTEM use manual pages from other systems
-M, --manpath=PATH set search path for manual pages to PATH
-s, --section=SECTION search only this section
-?, --help give this help list
--usage give a short usage message
-V, --version print program version
Mandatory or optional arguments to long options are also mandatory or optional
for any corresponding short options.
The --regex option is enabled by default.
Report bugs to cjwatson@debian.org.
Particularly, the -e switch is quite useful to filter out your search. See the example below:
samar@Techgaun:~$ apropos -e tar bf_tar (1) - shell script to write a tar file of a bogofilter direc... bf_tar-bdb (1) - shell script to write a tar file of a bogofilter direc... git-tar-tree (1) - Create a tar archive of the files in the named tree ob... lz (1) - gunzips and shows a listing of a gzip'd tar'd archive mxtar (1) - Wrapper for using GNU tar directly from a floppy disk ptar (1) - a tar-like program written in perl tar (1) - The GNU version of the tar archiving utility tar (5) - format of tape archive files tgz (1) - makes a gzip'd tar archive uz (1) - gunzips and extracts a gzip'd tar'd archive
Each command has its associated short description and the apropos command searches the short description section of appropriate manual page for the provided keyword. You can also specify the search keywords in the form of regular expression for more flexibility. I hope this command counts as useful one :)
Read more...
How To Search Manual Pages In Linux
2012-09-02T02:07:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|edubuntu|fedora|linux|tricks and tips|ubuntu|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
edubuntu,
fedora,
linux,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Friday, 27 July 2012
Determine Your SATA Disk Model And Vendor In Ubuntu
Sometimes you need to determine the model and vendor of your hard disk and here is the small tips on how to find those information.
All you have to do is type one of the following commands for the respective outputs:
I hope this becomes useful sometimes. :)
Read more...
All you have to do is type one of the following commands for the respective outputs:
cat /sys/class/block/sda/device/model
cat /sys/class/block/sda/device/vendor
Read more...
Determine Your SATA Disk Model And Vendor In Ubuntu
2012-07-27T21:36:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|linux|ubuntu|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
linux,
ubuntu
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Wednesday, 18 July 2012
Why Alias Command With Itself
Aliasing the command to itself to suppress the original functionality of the command and provide it new added sets of functionality can come quite handy for linux users and administrators.
If you have been using linux shell for a while, I'm pretty sure you are now familiar with the `ls` command, if not I think you have just learnt to use man pages. Probably you've been using `ls -l` command to list files with the files size as well. Too bad, you won't just be able to instantly make the sense of the file size displayed using this command so why not alias `ls` command to always provide human readable file sizes. So here is my alias:
This is what I always want to see as the output with `ls` command. The same kind of alias can be used with `du` and `df` commands. There are number of other cases where aliasing a command with itself is good choice.
Another example is the less command. By default, you need to press q to exit less which can be quite annoying if the entire content can fit in a single screen. However, adding -F flag will gracefully quit after displaying the content if the content fits in a single screen. So I have my alias for less as below:
If something shoots in your mind, feel free to share here as a comment :)
Read more...
If you have been using linux shell for a while, I'm pretty sure you are now familiar with the `ls` command, if not I think you have just learnt to use man pages. Probably you've been using `ls -l` command to list files with the files size as well. Too bad, you won't just be able to instantly make the sense of the file size displayed using this command so why not alias `ls` command to always provide human readable file sizes. So here is my alias:
alias ls='ls -lh'
This is what I always want to see as the output with `ls` command. The same kind of alias can be used with `du` and `df` commands. There are number of other cases where aliasing a command with itself is good choice.
Another example is the less command. By default, you need to press q to exit less which can be quite annoying if the entire content can fit in a single screen. However, adding -F flag will gracefully quit after displaying the content if the content fits in a single screen. So I have my alias for less as below:
alias lesss='less -F'
If something shoots in your mind, feel free to share here as a comment :)
Read more...
Why Alias Command With Itself
2012-07-18T18:15:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|edubuntu|fedora|linux|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
edubuntu,
fedora,
linux,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Friday, 6 July 2012
Fix "trying to overwrite '*', which is also in package *"
Today I was updating few stuffs in edubuntu and dpkg was continually throwing me the problem while trying to install kdelibs-data. The error read as "trying to overwrite 'A', which is also in package X" and the fix was pretty straightforward but still I thought it would help someone out there.
Below is the exact error I was getting while trying to install kdelibs5-data from the deb file.
The fix was pretty simple. Add the --force-overwrite switch in the dpkg command as below:
I hope this comes useful sometimes.
Read more...
Below is the exact error I was getting while trying to install kdelibs5-data from the deb file.
dpkg: error processing /var/cache/apt/archives/
kdelibs5-data_4%3a4.4.5-0ubuntu1.2_all.deb (--unpack):
trying to overwrite '/usr/share/polkit-1/actions
/org.kde.kcontrol.kcmremotewidgets.policy', which is also in package kdebase-runtime-data 4:4.6.5-0ubuntu1
kdelibs5-data_4%3a4.4.5-0ubuntu1.2_all.deb (--unpack):
trying to overwrite '/usr/share/polkit-1/actions
/org.kde.kcontrol.kcmremotewidgets.policy', which is also in package kdebase-runtime-data 4:4.6.5-0ubuntu1
The fix was pretty simple. Add the --force-overwrite switch in the dpkg command as below:
dpkg -i --force-overwrite kdelibs5-data_4.4.5-0ubuntu1.2_all.deb
I hope this comes useful sometimes.
Read more...
Fix "trying to overwrite '*', which is also in package *"
2012-07-06T17:34:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|edubuntu|linux|ltsp|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
edubuntu,
linux,
ltsp,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Friday, 15 June 2012
Recover Deleted Files From An NTFS Volume Using Ntfsundelete
Ntfsundelete is a part of ntfsprogs, a suite of NTFS utilities based around a shared library. It lets us recover the deleted files from any NTFS volumes without making any changes in the NTFS volume itself.
Generally when a file is deleted from disks, it is some kind of pointer to the physical file that gets deleted and the actual content still remains in the disk unless it is overwritten by new files so it is possible to recover those files.
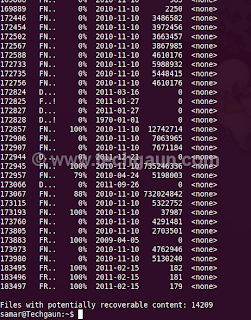
ntfsundelete has three modes of operation: scan, undelete and copy. By default, it will run in the scan mode which simply reads an NTFS volume and looks for the files that have been deleted.
To use ntfsundelete, you'll have to install the ntfsprogs suite with following command in ubuntu and debian-based distros:
You'll have to first figure out which drive you want to recover. A handy command for this is:
Once you know the NTFS volume you want to recover, you can first run the scan mode to list the filenames that can be recovered.
The optional -f switch can be specified for the forceful scanning. There is a nice percentage field which gives the information on how much of the file can be recovered. You can apply the time and percentage filters to scan specific files. For example, you can use the following command to search for the files which can be recovered 100%
And, you can apply the time filter to list the files altered/deleted after the specified time. For example, following command will scan and list the files deleted in the last 14 days.
Other suffices you can use are d, w, m, y for days, weeks, months or years ago respectively.
Once you get the files to be recovered, you can use the -u switch to undelete or recover the files. An example of recovering files by pattern matching is as below:
Similarly you can recover by providing inode or inodes range using the -i switch. You can get the inode values from the first column in the scan mode.
Read more...
Generally when a file is deleted from disks, it is some kind of pointer to the physical file that gets deleted and the actual content still remains in the disk unless it is overwritten by new files so it is possible to recover those files.
ntfsundelete has three modes of operation: scan, undelete and copy. By default, it will run in the scan mode which simply reads an NTFS volume and looks for the files that have been deleted.

To use ntfsundelete, you'll have to install the ntfsprogs suite with following command in ubuntu and debian-based distros:
samar@Techgaun:~$ sudo apt-get install ntfsprogs
You'll have to first figure out which drive you want to recover. A handy command for this is:
samar@Techgaun:~$ sudo fdisk -l
Once you know the NTFS volume you want to recover, you can first run the scan mode to list the filenames that can be recovered.
samar@Techgaun:~$ sudo ntfsundelete /dev/sda4
The optional -f switch can be specified for the forceful scanning. There is a nice percentage field which gives the information on how much of the file can be recovered. You can apply the time and percentage filters to scan specific files. For example, you can use the following command to search for the files which can be recovered 100%
samar@Techgaun:~$ sudo ntfsundelete -p 100 /dev/sda4
And, you can apply the time filter to list the files altered/deleted after the specified time. For example, following command will scan and list the files deleted in the last 14 days.
samar@Techgaun:~$ sudo ntfsundelete -p 100 -t 2d /dev/sda4
Other suffices you can use are d, w, m, y for days, weeks, months or years ago respectively.
Once you get the files to be recovered, you can use the -u switch to undelete or recover the files. An example of recovering files by pattern matching is as below:
samar@Techgaun:~$ sudo ntfsundelete -u -m *.jpg /dev/sda4
Similarly you can recover by providing inode or inodes range using the -i switch. You can get the inode values from the first column in the scan mode.
samar@Techgaun:~$ sudo ntfsundelete -u -i 161922 /dev/sda4
Read more...
Recover Deleted Files From An NTFS Volume Using Ntfsundelete
2012-06-15T16:08:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|fedora|linux|ntfs|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
fedora,
linux,
ntfs,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Sunday, 27 May 2012
Accelerate Download Speed In Linux Using Axel
Axel is a lightweight command line download accelerator for linux. Axel is a program that downloads a file from a FTP or HTTP server through multiple connection, each connection downloads its own part of the file.
Unlike most other programs, Axel downloads all the data directly to the destination file, using one single thread. It just saves some time at the end because the program doesn't have to concatenate all the downloaded parts.
Axel tries to accelerate downloads by using multiple connections (possibly to multiple servers) for one download. Because of its size, it might be very useful on bootdisks or other small systems as a wget replacement.
One useful implementation of axel is in the apt-fast tool, a fusion of apt-get and axel to accelerate downloads of packages.
Installation under ubuntu and other debian distros: Open the terminal and type:
Similarly, a graphical frontend axel-kapt is also available for download for GUI lovers. Also, flashgot plugin for firefox lets you make use of axel to download files. I should say, axel is a small yet good download accelerator for linux systems.
Read more...
Unlike most other programs, Axel downloads all the data directly to the destination file, using one single thread. It just saves some time at the end because the program doesn't have to concatenate all the downloaded parts.
Axel tries to accelerate downloads by using multiple connections (possibly to multiple servers) for one download. Because of its size, it might be very useful on bootdisks or other small systems as a wget replacement.
One useful implementation of axel is in the apt-fast tool, a fusion of apt-get and axel to accelerate downloads of packages.
Installation under ubuntu and other debian distros: Open the terminal and type:
sudo apt-get install axel
Similarly, a graphical frontend axel-kapt is also available for download for GUI lovers. Also, flashgot plugin for firefox lets you make use of axel to download files. I should say, axel is a small yet good download accelerator for linux systems.
Read more...
Accelerate Download Speed In Linux Using Axel
2012-05-27T21:38:00+05:45
Cool Samar
axel|command line|download|linux|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
axel,
command line,
download,
linux,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)


